Datei:Guam ali 2011364 lrg.jpg
Originaldatei (3.994 × 5.148 Pixel, Dateigröße: 4,36 MB, MIME-Typ: image/jpeg)
Diese Datei stammt aus Wikimedia Commons und kann von anderen Projekten verwendet werden. Die Beschreibung von deren Dateibeschreibungsseite wird unten angezeigt.
Beschreibung
| BeschreibungGuam ali 2011364 lrg.jpg |
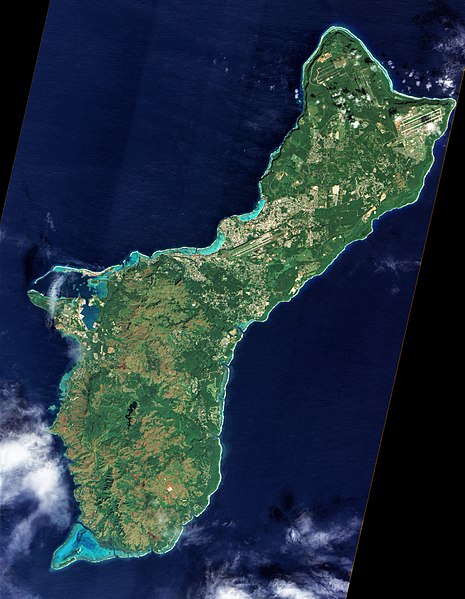
English: On December 30, 2011, cloud-free skies presented NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite with this unobstructed view of the island of Guam. Note that this image, taken by the satellite’s Advanced Land Imager (ALI), has been rotated and north is at right.
Located in the tropical Pacific Ocean, the U.S. territory of Guam lies at the southern end of the Mariana Island Chain. As the largest island in that archipelago, Guam stretches roughly 30 miles (50 kilometers) from northeast to southwest. Fields, forests, military bases, and settlements all mix on the landscape. Two prominent airstrips run northeast-southwest, one at the northeastern tip of the island, and the other in central Guam. Guam has two seasons: wet (June to December) and dry (January to June), and ALI acquired this image during the transition from wet to dry. The fate of that rainwater has a lot to do with whether it lands in the northern or southern part of the island. In southern Guam, volcanic rock predominates, but in northern Guam, limestone overlies volcanic rock. Limestone is porous—so porous, in fact, that practically all the water in northern Guam infiltrates the rock. After percolating through the limestone, water in northern Guam becomes part of the groundwater system. Guam’s rivers are confined to the southern part of the island, where less porous volcanic rock enables water to collect on the surface. Coral reefs fringe the island, and they are especially visible around Apra Harbor and Cocos Lagoon. Shallow water along these reefs glows peacock blue. Not far from Guam, the ocean is anything but shallow. Just east of the Mariana Islands lies the Mariana Trench. Located at the boundary between tectonic plates, it is the deepest point in the Earth’s ocean. References
NASA Earth Observatory image created by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team and the United States Geological Survey. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI |
|||
| Datum | ||||
| Quelle | http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=77189 | |||
| Urheber | NASA | |||
| Andere Versionen |
|
Lizenz
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| Diese Datei ist gemeinfrei (public domain), da sie von der NASA erstellt worden ist. Die NASA-Urheberrechtsrichtlinie besagt, dass „NASA-Material nicht durch Urheberrecht geschützt ist, wenn es nicht anders angegeben ist“. (NASA-Urheberrechtsrichtlinie-Seite oder JPL Image Use Policy). |  | |
 |
Warnung:
|
Kurzbeschreibungen
In dieser Datei abgebildete Objekte
Motiv
30. Dezember 2011
image/jpeg
Dateiversionen
Klicke auf einen Zeitpunkt, um diese Version zu laden.
| Version vom | Vorschaubild | Maße | Benutzer | Kommentar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aktuell | 10:16, 24. Mai 2020 |  | 3.994 × 5.148 (4,36 MB) | wikimediacommons>Beyond My Ken | Adjs for visibility |
Dateiverwendung
Die folgende Seite verwendet diese Datei:
Metadaten
Diese Datei enthält weitere Informationen, die in der Regel von der Digitalkamera oder dem verwendeten Scanner stammen. Durch nachträgliche Bearbeitung der Originaldatei können einige Details verändert worden sein.
| Bildtitel |
|
|---|---|
| Breite | 5.491 px |
| Höhe | 11.161 px |
| Bits pro Farbkomponente |
|
| Art der Kompression | LZW |
| Pixelzusammensetzung | RGB |
| Kameraausrichtung | Normal |
| Anzahl Komponenten | 3 |
| Horizontale Auflösung | 100 dpi |
| Vertikale Auflösung | 100 dpi |
| Datenausrichtung | Grobformat |
| Software | Windows Photo Editor 10.0.10011.16384 |
| Speicherzeitpunkt | 04:15, 24. Mai 2020 |
| Farbraum | sRGB |
| Digitalisierungszeitpunkt | 07:48, 1. Feb. 2012 |
| Datum zu dem die Metadaten letztmalig geändert wurden | 06:30, 16. Feb. 2012 |
| Eindeutige Kennung des ursprünglichen Dokuments | xmp.did:FB7F117407206811AA97CCED880B21C1 |
